概述
Tomcat中最重要的两大组件:Connector 和 Container,Connector 负责接收网络请求,然后转换为 Servlet 请求。一个 Tomcat 可以配置多个 Connector,分别用于监听不同端口,或处理不同协议。
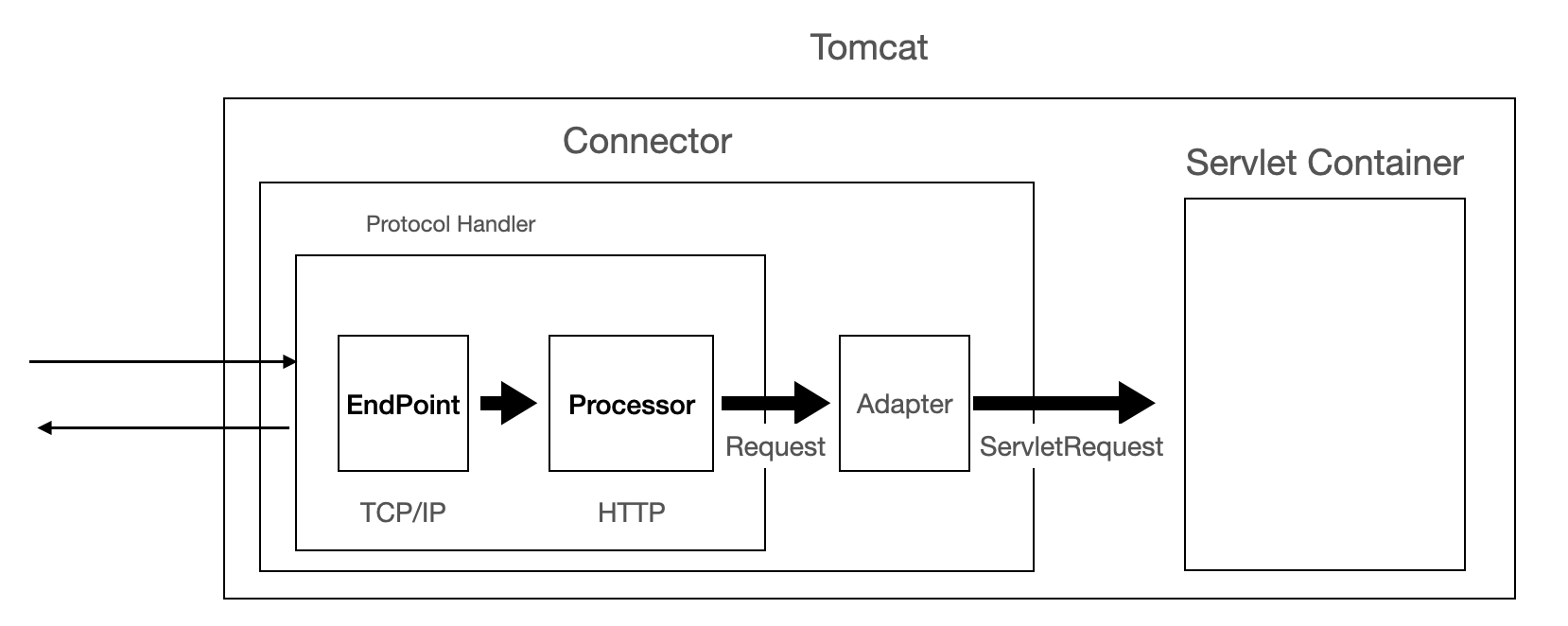
Connector 负责接收浏览器的发过来的 TCP 连接请求,创建一个 Request 和 Response 对象分别用于和请求端交换数据,并把产生的 Request 和 Response 对象封装提交到线程池,而处理请求的逻辑则是 Container 组件要做的事了。本文不涉及 Container,重点是 NIO Connector,源码基于 Tomcat 9.0.17。
在 Connector 的构造方法中,我们可以传 HTTP/1.1 或 AJP/1.3 等等用于指定协议,也可以传入相应的协议处理类。
- org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol:对应非阻塞 IO
- org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Nio2Protocol:对应异步 IO
- org.apache.coyote.http2.Http2Protocol:对应 Http2 协议
public Connector(String protocol) {
boolean aprConnector = AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable() &&
AprLifecycleListener.getUseAprConnector();
if ("HTTP/1.1".equals(protocol) || protocol == null) {
if (aprConnector) {
protocolHandlerClassName = "org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11AprProtocol";
} else {
protocolHandlerClassName = "org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol";
}
} else if ("AJP/1.3".equals(protocol)) {
if (aprConnector) {
protocolHandlerClassName = "org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpAprProtocol";
} else {
protocolHandlerClassName = "org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol";
}
} else {
protocolHandlerClassName = protocol;
}
...
}
Tomcat 各版本对 Connector 的迭代:
- Tomcat 4.1 只有 Java BIO Connector
- Tomcat 5.5 添加了 Apache Portable Runtime (APR) Connector
- Tomcat 6.0 添加了 NIO 连接器
- Tomcat 8.0 添加了 NIO2 连接器
- Tomcat 9.0 放弃了 BIO ****Connector
- Tomcat 9.0 添加了通过 NIO 和 NIO2 使用 OpenSSL 进行 TLS 的功能
BIO Connector
Http11Protocol 表示 BIO (Blocking IO) 的 HTTP 协议的通信,在Tomcat 9中,BIO 模式的实现 Http11Protocol 已经被删除了。
下图是 BIO Connector 的总体执行流程:
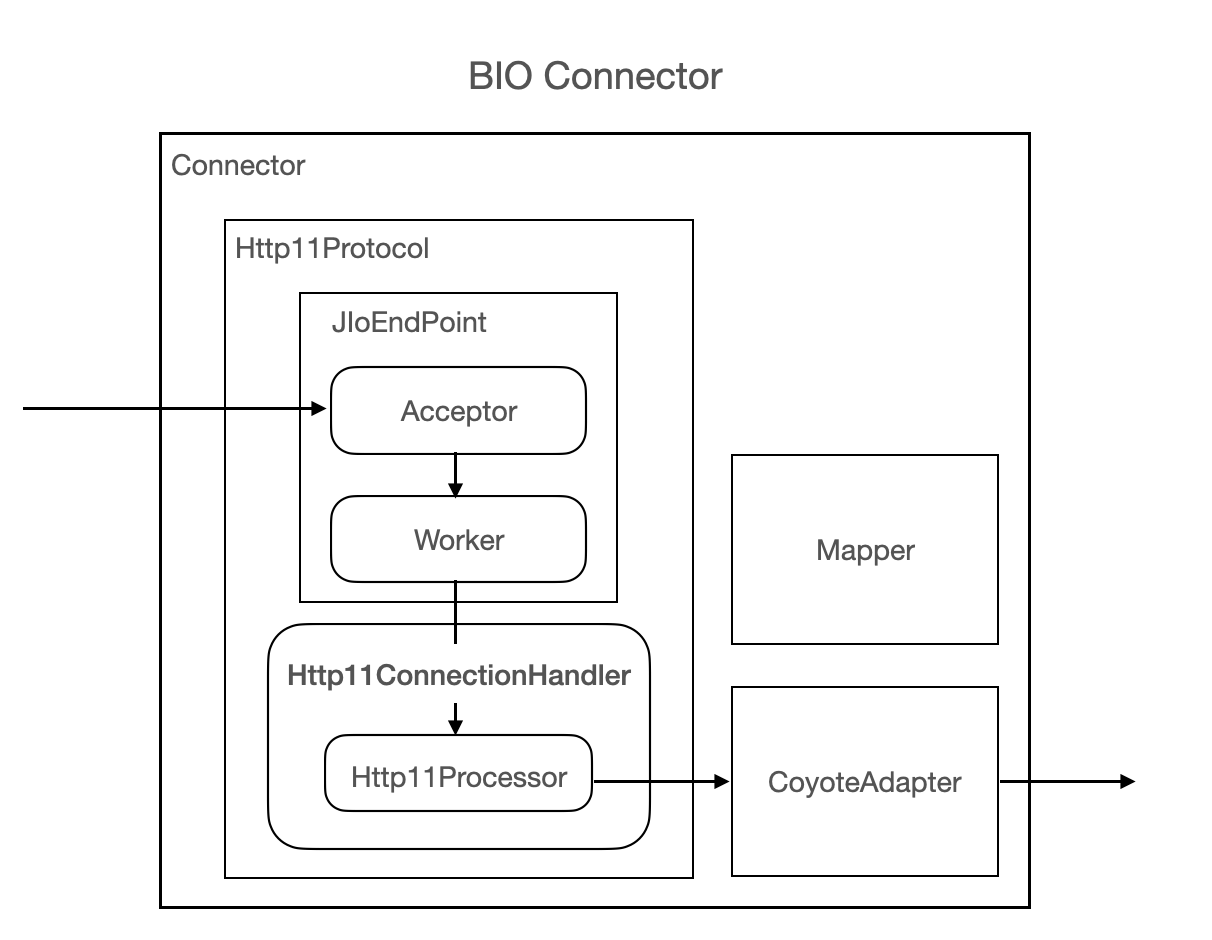
- BIO Connector 启动 JIoEndPoint 绑定服务端口,监听 HTTP/1.1 协议请求
- 然后启动若干 Acceptor 线程用于接收 Socket 连接,
- 然后封装为 SocketProcessor 提交到工作线程池处理,
- SocketProcessor 读取 Socket 字节流根据协议解析为标准 Servlet Request,请求到 Container 处理业务逻辑,响应请求、关闭 Socket等。
若工作线程池中没有空闲的线程,那么 Acceptor 将会阻塞,这里是和 NIO 最大区别,线程数量制约了并发数。并且由于获取到新连接后,连接并不一定是就绪(虽然已连接,但数据还没到达)状态,导致处理请求的线程可能很大一部分时间是空闲状态。
Tomcat 中的
ThreadPoolExecutor继承自 JDK 线程池并进行了部分策略修改。包括创建时启动 core 数量线程,自定义TaskQueue使任务提交时优先达到 maxPoolSize 线程数、超过再入队列等等。
NIO Connector
Tomcat5 及以后版本开始支持 NIO Connector。NIO Connector 在获取到新连接时,不会立即分配到线程池,而是将 Connection(Channel)传给 Poller 线程。Poller 将 Socket 保存为缓存,只有当 Socket 中可以处理数据(就绪)时才分配线程,从而减少线程空闲时浪费的时间。
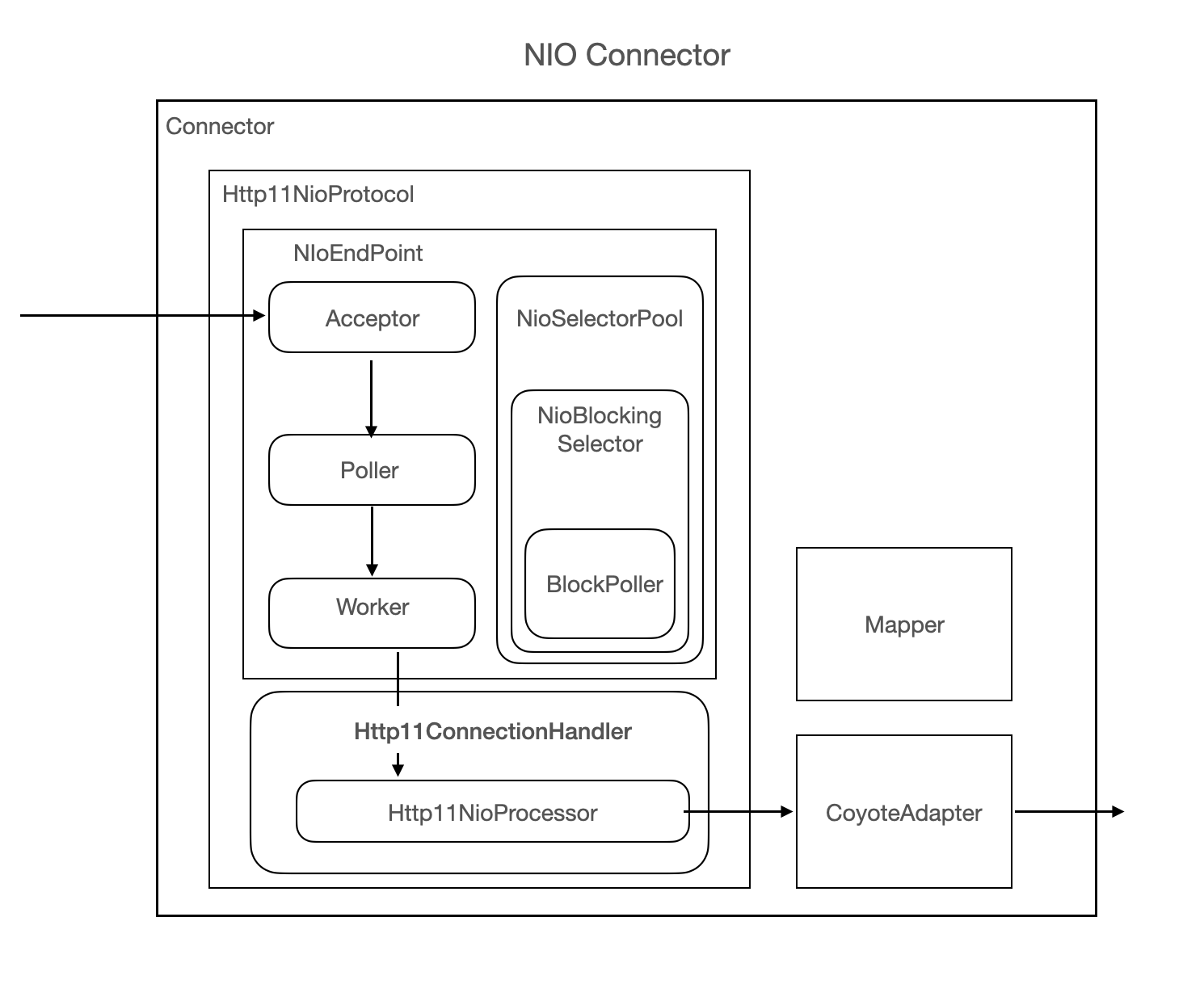
NIO 启动流程(摘取从 org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat#start 开始的关键代码):
- 绑定服务器端口。
public void bind() throws Exception { // 绑定地址、端口 initServerSocket(); // acceptorThread 默认 1 // Initialize thread count defaults for acceptor, poller if (acceptorThreadCount == 0) { // FIXME: Doesn't seem to work that well with multiple accept threads acceptorThreadCount = 1; } // pollerThreadCount 多核默认 2 // Math.min(2,Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()) if (pollerThreadCount <= 0) { //minimum one poller thread pollerThreadCount = 1; } setStopLatch(new CountDownLatch(pollerThreadCount)); // Initialize SSL if needed initialiseSsl(); selectorPool.open(); } protected void initServerSocket() throws Exception { if (!getUseInheritedChannel()) { serverSock = ServerSocketChannel.open(); socketProperties.setProperties(serverSock.socket()); InetSocketAddress addr = new InetSocketAddress(getAddress(), getPortWithOffset()); // 绑定地址、端口 serverSock.socket().bind(addr,getAcceptCount()); } else { // Retrieve the channel provided by the OS Channel ic = System.inheritedChannel(); if (ic instanceof ServerSocketChannel) { serverSock = (ServerSocketChannel) ic; } if (serverSock == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("endpoint.init.bind.inherited")); } } // 设置为阻塞模式, 后续调用 accept() 时会阻塞等待可用连接 serverSock.configureBlocking(true); //mimic APR behavior } - 启动工作线程池、Poller 、Acceptor 线程组等。
public void startInternal() throws Exception { if (!running) { running = true; paused = false; // 初始化缓存实现对象复用 processorCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE, socketProperties.getProcessorCache()); eventCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE, socketProperties.getEventCache()); nioChannels = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE, socketProperties.getBufferPool()); // Create worker collection if ( getExecutor() == null ) { // 启动线程池 createExecutor(); } // 初始化连接数限制 默认 10000 initializeConnectionLatch(); // Start poller threads pollers = new Poller[getPollerThreadCount()]; for (int i=0; i<pollers.length; i++) { pollers[i] = new Poller(); Thread pollerThread = new Thread(pollers[i], getName() + "-ClientPoller-"+i); pollerThread.setPriority(threadPriority); pollerThread.setDaemon(true); pollerThread.start(); } // 启动 Acceptor 线程,和 poller 线程一样默认守护线程 startAcceptorThreads(); } } - Acceptor
public void run() { ... 省略部分代码 // Loop until we receive a shutdown command while (endpoint.isRunning()) { ... state = AcceptorState.RUNNING; try { //if we have reached max connections, wait endpoint.countUpOrAwaitConnection(); ... U socket = null; try { // Accept the next incoming connection from the server socket **// 获取连接(endpoint 初始化时已置为阻塞模式,所以这里会阻塞)** socket = endpoint.serverSocketAccept(); } catch (Exception ioe) { // We didn't get a socket endpoint.countDownConnection(); if (endpoint.isRunning()) { // Introduce delay if necessary errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay); // re-throw throw ioe; } else { break; } } ... // Configure the socket if (endpoint.isRunning() && !endpoint.isPaused()) { // setSocketOptions() will hand the socket off to // an appropriate processor if successful **// 处理连接** if (!endpoint.setSocketOptions(socket)) { endpoint.closeSocket(socket); } } else { endpoint.destroySocket(socket); } } catch (Throwable t) { ... } state = AcceptorState.ENDED; }关键就是调用了
ServerSocketChannel#accept获取新连接以及NioEndpoint#setSocketOptions处理连接 -
处理 connection
protected boolean setSocketOptions(SocketChannel socket) { // Process the connection try { //disable blocking, APR style, we are gonna be polling it socket.configureBlocking(false); Socket sock = socket.socket(); socketProperties.setProperties(sock); // 从缓冲池取一个 NioChannel NioChannel channel = nioChannels.pop(); if (channel == null) { SocketBufferHandler bufhandler = new SocketBufferHandler( socketProperties.getAppReadBufSize(), socketProperties.getAppWriteBufSize(), socketProperties.getDirectBuffer()); if (isSSLEnabled()) { channel = new SecureNioChannel(socket, bufhandler, selectorPool, this); } else { channel = new NioChannel(socket, bufhandler); } } else { channel.setIOChannel(socket); channel.reset(); } // getPoller0() 返回(轮询)某一个 poller,register 见下面几行 getPoller0().register(channel); } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); try { log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.socketOptionsError"), t); } catch (Throwable tt) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(tt); } // Tell to close the socket return false; } return true; } // Poller 注册 socket,并且新建 PollerEvent 加入到该 Poller event 队列(由于这里调用到了,代码提前到这里来介绍) public void register(final NioChannel socket) { socket.setPoller(this); NioSocketWrapper ka = new NioSocketWrapper(socket, NioEndpoint.this); socket.setSocketWrapper(ka); ka.setPoller(this); ka.setReadTimeout(getConnectionTimeout()); ka.setWriteTimeout(getConnectionTimeout()); ka.setKeepAliveLeft(NioEndpoint.this.getMaxKeepAliveRequests()); ka.setSecure(isSSLEnabled()); PollerEvent r = eventCache.pop(); ka.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);//this is what OP_REGISTER turns into. // OP_REGISTER 很关键,代表新连接,后面执行 event 时会用到 if ( r==null) r = new PollerEvent(socket,ka,OP_REGISTER); else r.reset(socket,ka,OP_REGISTER); addEvent(r); }主要就是将 NioChannel 注册到 Poller,此时 Acceptor 任务完成,继续处理新连接。
-
Poller
public class Poller implements Runnable { // 关联的 selector private Selector selector; // events 队列,Poller 的核心 private final SynchronizedQueue<PollerEvent> events = new SynchronizedQueue<>(); private volatile boolean close = false; private long nextExpiration = 0;//optimize expiration handling private AtomicLong wakeupCounter = new AtomicLong(0); private volatile int keyCount = 0; public Poller() throws IOException { this.selector = Selector.open(); } NioEndpoint.Poller#runpublic void run() { // Loop until destroy() is called while (true) { boolean hasEvents = false; try { if (!close) { // 执行 events 队列中每个 event 的 run() 方法,下面有介绍该方法 hasEvents = events(); // wakeupCounter 的初始值为 0,这里置为 -1,返回旧值 if (wakeupCounter.getAndSet(-1) > 0) { //if we are here, means we have other stuff to do //do a non blocking select keyCount = selector.selectNow(); } else { keyCount = selector.select(selectorTimeout); } wakeupCounter.set(0); } if (close) { ... } } catch (Throwable x) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(x); log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.selectorLoopError"), x); continue; } //either we timed out or we woke up, process events first if ( keyCount == 0 ) hasEvents = (hasEvents | events()); // 若 select 返回 > 0, 那么迭代处理 ready keys Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null; // Walk through the collection of ready keys and dispatch // any active event. while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey sk = iterator.next(); NioSocketWrapper attachment = (NioSocketWrapper)sk.attachment(); // Attachment may be null if another thread has called // cancelledKey() if (attachment == null) { iterator.remove(); } else { iterator.remove(); // 处理 ready selectionKey processKey(sk, attachment); } }//while //process timeouts timeout(keyCount,hasEvents); }//while getStopLatch().countDown(); }NioEndpoint.PollerEvent#runpublic void run() { // 对应新注册连接的 event interestOps 类型 if (interestOps == OP_REGISTER) { try { // 将当前新连接 SocketChannel 注册到该 Poller 的 selector 中 // 并监听 OP_READ 事件 // 之后上面的 Poller.run 中会处理对应 readable 事件 socket.getIOChannel().register( socket.getPoller().getSelector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ, socketWrapper); } catch (Exception x) { log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.registerFail"), x); } } else { ... } }NioEndpoint.Poller#processKeyprotected void processKey(SelectionKey sk, NioSocketWrapper attachment) { try { if ( close ) { cancelledKey(sk); } else if ( sk.isValid() && attachment != null ) { if (sk.isReadable() || sk.isWritable() ) { if ( attachment.getSendfileData() != null ) { processSendfile(sk,attachment, false); } else { // 接下来是处理 SocketChannel 进来的数据,所以不再监听该 channel 的 OP_READ 事件 // unregister 相应的 interest set, unreg(sk, attachment, sk.readyOps()); boolean closeSocket = false; // Read goes before write if (sk.isReadable()) { // 处理读请求 if (!processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ, true)) { closeSocket = true; } } if (!closeSocket && sk.isWritable()) { // 处理写请求 if (!processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE, true)) { closeSocket = true; } } if (closeSocket) { cancelledKey(sk); } } } } else { //invalid key cancelledKey(sk); } } catch ( CancelledKeyException ckx ) { cancelledKey(sk); } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.keyProcessingError"), t); } }AbstractEndpoint#processSocketpublic boolean processSocket(SocketWrapperBase<S> socketWrapper, SocketEvent event, boolean dispatch) { try { if (socketWrapper == null) { return false; } SocketProcessorBase<S> sc = processorCache.pop(); if (sc == null) { // 这里会返回 SocketProcessor,多么熟悉,后面和 BIO 差不多了 sc = createSocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event); } else { sc.reset(socketWrapper, event); } Executor executor = getExecutor(); if (dispatch && executor != null) { // socketProcessor 提交到线程池,解析...执行业务逻辑...响应 executor.execute(sc); } else { sc.run(); } } catch (RejectedExecutionException ree) { getLog().warn(sm.getString("endpoint.executor.fail", socketWrapper) , ree); return false; } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); // This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that // the pool and its queue are full getLog().error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t); return false; } return true; }
NioEndpoint 处理流程
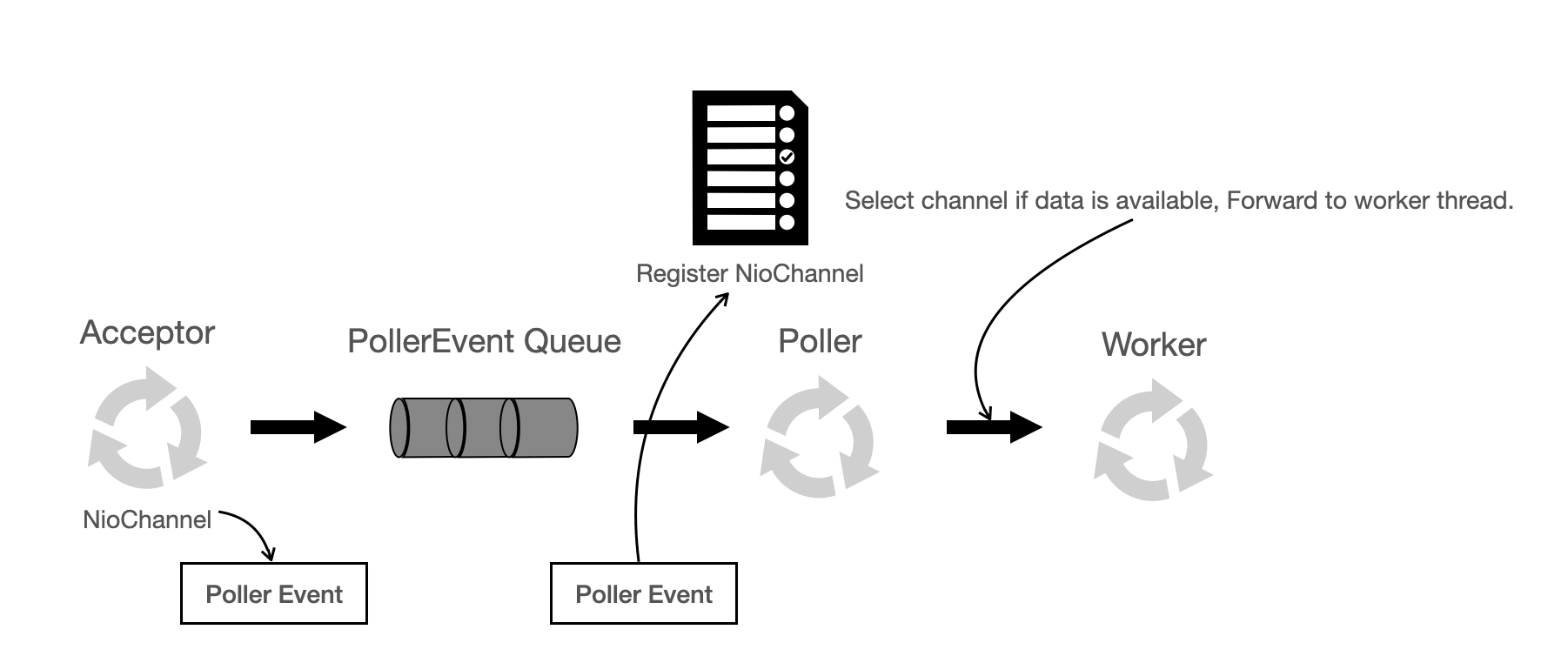
- 指定 Protocol,初始化相应的 Endpoint,例如 NioEndpoint;
- init 过程:在 NioEndpoint 中做 bind 操作;
- start 过程:启动 worker 线程池,启动 1 个 Acceptor 和 2 个 Poller 可配置数量;
- Acceptor 获取到新的连接后,getPoller0() 获取其中一个 Poller,然后 register 到 Poller 中;
- Poller 循环 selector.select(xxx),如果有通道 readable,那么在 processKey 中将其放到 worker 线程池中。
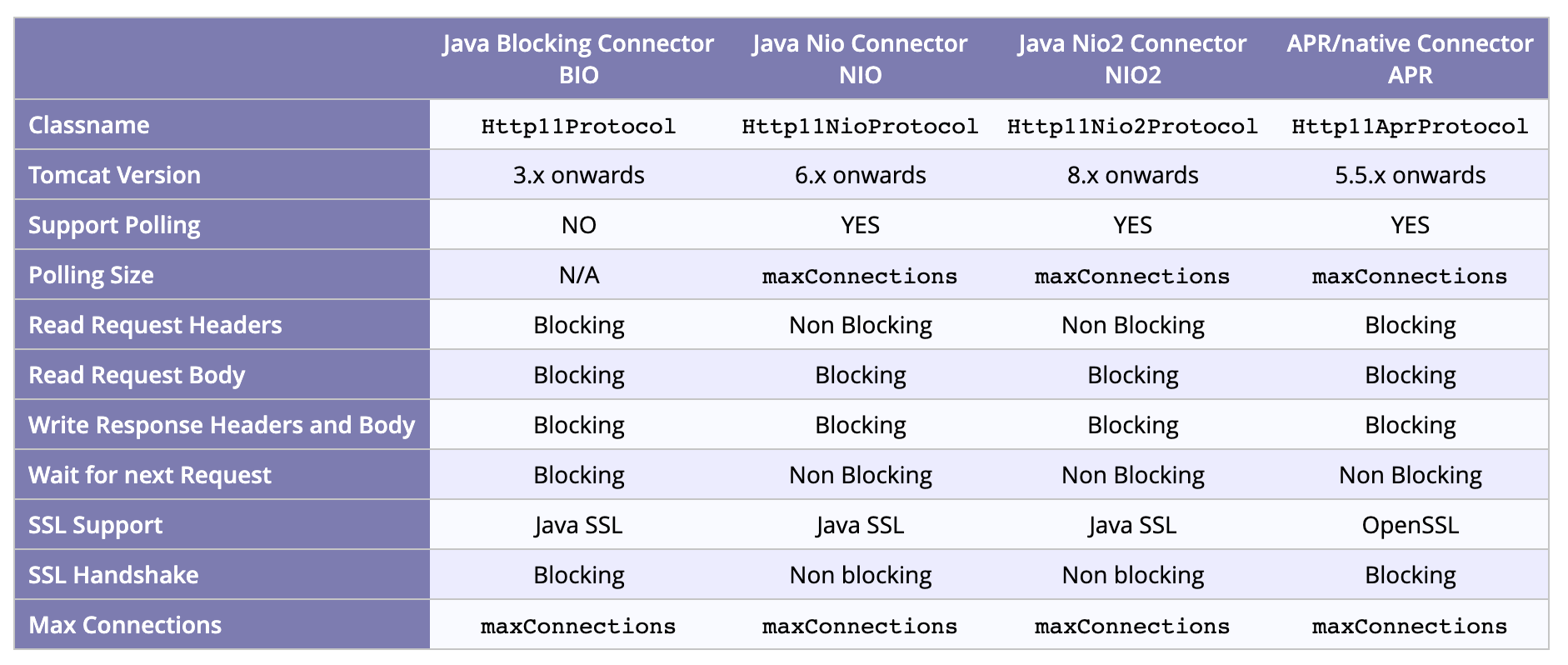
各协议 Connector 对比
NIO 对比 BIO
所谓的 I/O 就是计算机内存与外部设备之间拷贝数据的过程,对于一个网络I/O通信过程,比如网络数据读取,会涉及两个对象,一个是调用这个I/O操作的用户线程,另外一个就是操作系统内核。一个进程的地址空间分为用户空间和内核空间,用户线程不能直接访问内核空间。
当用户线程发起I/O操作后,网络数据读取操作会经历两个步骤:
- 用户线程等待内核将数据从网卡拷贝到内核空间。
- 内核将数据从内核空间拷贝到用户空间。
NIO 对比 BIO 的区别就是:它们实现这两个步骤的方式是不一样的。
- 对于 BIO:用户线程发起read调用后就阻塞了,让出CPU。内核等待网卡数据到来,把数据从网卡拷贝到内核空间,接着把数据拷贝到用户空间,再把用户线程叫醒。
- 对于 NIO:用户线程的读取操作分成两步了,线程先发起select调用,目的是问内核数据准备好了吗?等内核把数据准备好了,用户线程再发起read调用。在等待数据从内核空间拷贝到用户空间这段时间里,线程还是阻塞的。那为什么叫I/O多路复用呢?因为一次select调用可以向内核查多个数据通道(Channel)的状态,所以叫多路复用。
基于 Selecoter 的 IO 多路复用机制可以使得 Tomcat NIO 同时处理的 Socket 数目远大于最大线程数,并发性能大大提高。
BIO 和 NIO 在真正的读取和响应数据的时候都是阻塞的(Read Request Body 和 Write Response Headers and Body),而 NIO 由于采用多路复用模型,在等待下一次请求的时候(Wait for next Request)是非阻塞的。
但是 NIO 在读取请求头(Read Request Headers)的时候可以做到非阻塞,因为 NIO 调用 SocketChannel.read() 读取请求头和请求行信息,读取不到会立即返回 0,线程不会阻塞,由 Poller继续监测下次数据的到来。而 NIO 对于请求体的读取是阻塞的读取,如果发现请求体数据不可读,那么首先注册 OP_READ 事件到 BlockPoller对象实例的事件队列里,然后阻塞此 Worker 线程。
总结
在对比 NIO 和 BIO 后,总结下对于 IO 模型的优化是如何支撑高并发的:
- 高并发就是能快速地处理大量的请求,需要合理设计线程模型让 CPU 忙起来,尽量不要让线程阻塞,因为一阻塞,CPU就闲下来了。
- 另外就是有多少任务,就用相应规模的线程数去处理。我们注意到NioEndpoint要完成三件事情:接收连接、检测 I/O 事件以及处理请求,那么最核心的就是把这三件事情分开,用不同规模的线程数去处理,比如用专门的线程组去跑 Acceptor,并且 Acceptor 的个数可以配置;用专门的线程组去跑 Poller,Poller 的个数也可以配置;最后具体任务的执行也由专门的线程池来处理,也可以配置线程池的大小。
